Apr 05, 2019 Favoring hardware RAID over software RAID comes from a time when hardware was just not powerful enough to handle Software RAID processing, along with all the other tasks that it was being used for. Back then, the solution was to use a hardware RAID card with a built-in processor that handled the RAID calculations ‘offline’. I have scoured through articles written about tuning software and I have used Linux software RAID for over 10 years. When running basic I/O tests (dd-oflag=direct 5k to 100G files, hdparam -t, etc.), software RAID seems to stack up favorably to hardware raid. The software RAID.
- Software Raid Vs Hardware Raid Machines
- Raid Software Free
- Raid System For Mac
- Hardware Raid 1
- Software Raid Vs Hardware Raid Mac Pro
- Mac Software Raid Vs Hardware Raid
An RAID array is a storage solution that combines multiple hard drives into one unit for the purpose of storing, backing up, and providing redundancy and security. RAID 5, with disk striping and parity, is ideal for use as a file-storage server or application server. This choice for Mac users requires a minimum of three drives and provides fault tolerance and good performance.
Summary :
Do you know what hardware and software RAID is? What is the difference between software RAID and hardware RAID? Hardware vs software RAID which one is better? If you are trying to figure them out, probably this post of MiniTool is suitable for you.
Quick Navigation :
To improve the performance, reliability, and capacity of your hard disk, the Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) is created. It is a data storage virtualization technology that can virtualize multiple independent hard disk drives into one or more arrays.
To analyze hardware vs software RAID, it is inevitable to talk about the dynamic volume. As you might know, the data on dynamic volume can be managed either by dedicated computer hardware or software.
Software Raid Vs Hardware Raid Machines
Implementing RAID needs to use either hardware RAID (special controller) or software RAID (an operating system driver). But a great many people are unclear about their differences. So, the following part will discuss the hardware vs software RAID to help you make a decision.
What are the differences between 10000 rpm HDD VS. SSD. How to upgrade your HDD to SSD without any data loss? Today’s article will tell you all the answers.
What Is Hardware RAID
Hardware RAID is a dedicated processing system that can be done completely on a separate RAID card/cabinet or the motherboard. With the hardware RAID setup, your hard drive can connect to a RAID controller card that is inserted in a fast PCle slot in a motherboard.
Hardware RAID controller can help you improve the performance since the processing is handled by the RAID card instead of the server. The hardware RAID card can work effectively in larger servers as well as on a desktop computer. In addition, writing backups and restoring data will produce less strain when using the hardware RAID card.
Based on the hardware system, the RAID subsystem can be managed independently from the host and only one single disk is provided for the host by per RAID array. For example, a hardware RAID device can connect to a SCSI controller and present the RAID array as a single SCSI drive.
You may have an overall understanding of hardware RAID. What is software RAID? Please keep reading.
What Is Software RAID
To compare software RAID vs hardware RAID, it’s also necessary to figure out what software RAID is. When your storage drives are directly connected to the server’s motherboard without a RAID controller, the RAID configuration will be managed by the utility software in the operating system. Here this process is referred to as the software RAID setup.
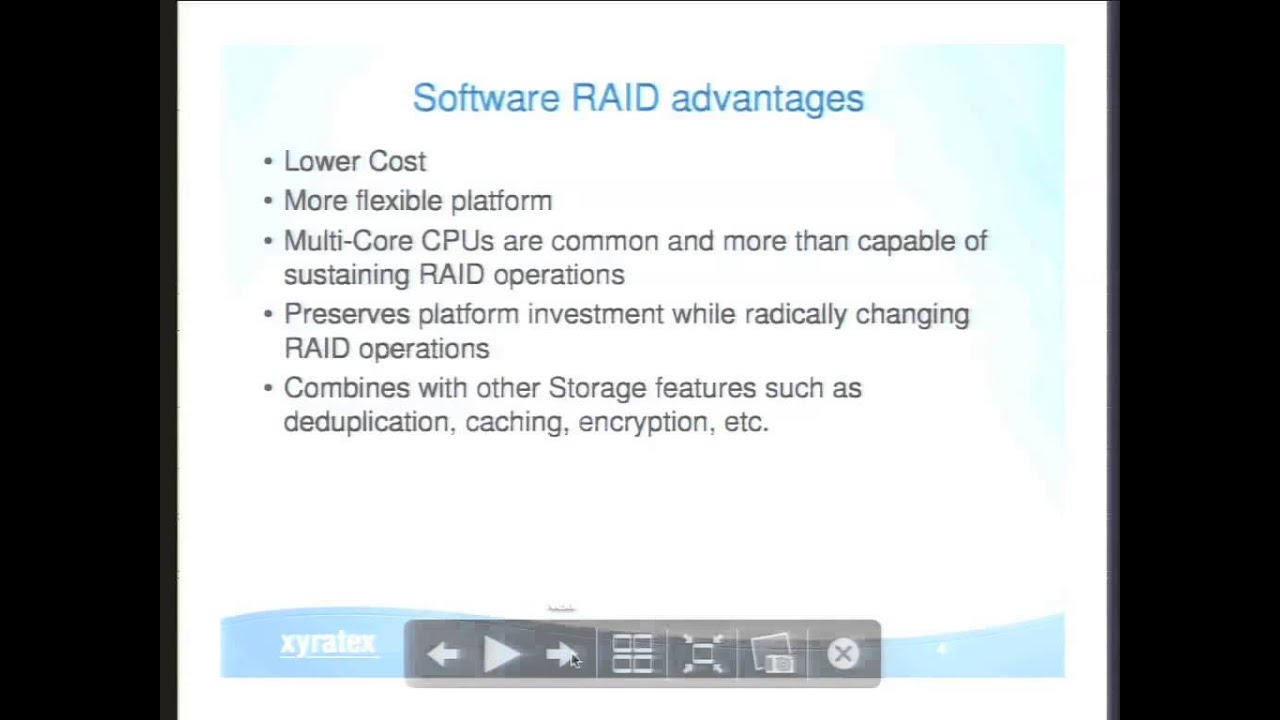
Software RAID setup is a cheaper choice compared with a hardware RAID controller. You are restricted to the RAID levels that your OS can support. In other words, software RAID has some limitations especially in terms of the configuration options.
Right now, you may have a preliminary impression of hardware vs software RAID according to the above information. Next, we will discuss the differences between software RAID and hardware RAID in detail.
mSATA and M.2 hard drive are both popular storage devices on the market. What’s the difference between mSATA and M.2? You can get the answer from the post.
Hardware VS Software RAID
The core of a RAID system is the controller, which plays an important role in distributing data to and from the hard drives that make up the RAID array. There are 2 types of RAID controllers including hardware-based and software-based.
So, the detailed information of hardware RAID vs software RAID will be analyzed based on the RAID controllers. To give you a better understanding, we will discuss the aspects of affordability, performance, and flexibility.
Affordability
As mentioned above, the software RAID controller is more affordable than the hardware RAID controller. In terms of affordability, you can refer to the form below to overview their differences.
Software RAID controller | Hardware RAID controller |
1. Lower price in general. 2. The basic RAID levels are supported by many operating systems. 3. The RAID levels are limited. If you want your hard drives to support RAID 3 and RAID 5, you need to purchase additional software. | 1. The hardware enclosures with built-in support for basic RAID levels are relatively affordable. 2. You still need to pay more money for the hardware enclosures that support advanced RAID levels and more hard drives. |
The RAID controller uses the computing power of your PC to control the way that the data is read or written to the enclosure. Since the hardware RAID enclosures can make full use of the standard interface chipsets, the manufacturing and design costs are relatively high.
But the software RAID controllers may be as low as zero since most basic RAID levels are included in many operating systems.
Performance
In general, the more complex your RAID configuration is, the more likely the performance will be affected. Compared with the hardware-based RAID systems, the software-based RAID systems are more likely to encounter a performance issue.
Software-based systems usually can perform adequately for 3 basic RAID levels including RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 10. However, when using more complex RAID levels, software-based RAID programs may impact the performance of the RAID system and the overall performance of your computer.
In addition, the hardware-based RAID systems will be quicker than software-based systems when rebuilding the mirrored RAID data. Here’s a form about the differences between hardware and software RAID systems in terms of performance.
Software RAID systems | Hardware RAID systems |
1. Perform adequately for basic RAID levels. 2. Performance may be affected by complex RAID levels. | 1. Performance equals to software-based systems for basic RAID levels. 2. Outperform the software-based systems for advanced RAID levels. 3. Rebuild mirrored RAID data much faster than software-based RAID systems. |
Flexibility
Apart from the affordability and performance, flexibility is also one aspect of hardware vs software RAID. The software-based RAID controllers are designed with the most flexibility in configuring the way that you use each drive in an enclosure.
In an enclosure with 4 drives, you’re allowed to configure 3 drives as a striped array for performance and one large drive for backup. Well, you can also configure the 4 drives as 2 independent arrays, a mirrored volume for gaming files, and a striped volume for video editing.
In other words, you can configure the 4 drives in an enclosure based on your needs. However, the hardware-based RAID systems work a single disk in the host operating system.
Raid Software Free
Software RAID controller | Hardware RAID controller |
1. Offer the most flexibility to have each drive configured in an enclosure. | 1. Work as a single disk to the host operating system. 2. It is easy to move an enclosure between computers and operating systems. |
Impact on Computer Performance
The differences between hardware and software RAID also have an important impact on computer performance.
With a software-based RAID controller, one or more CPU cores, as well as RAM could impact other processes that are running on your computer. The extent of the software RAID controller’s impact depends on the RAID level in use and the number of drives that makes up the RAID array.
However, if you are using an external hardware-based RAID enclosure, it will produce no impact on the processor or RAM on the host computer.
Many people don't know how to partition RAID 5 with reliable software. Read this post to see how to manage RAID with the best dynamic manger Minitool Partition Wizard.
Software RAID VS Hardware RAID: Which Is Better?
According to the above information, you may have an overall understanding of software RAID vs hardware RAID. Here comes a question – software vs hardware RAID which one is better?
Based on the data backup, the types of RAID will differ from system to system. Usually, it’s more common to see hardware RAID in Windows Server environments. This is because its advantages can be better realized in the Server.
Whereas software RAID is more prevalent in open-source server systems where its high flexibility and comparatively low cost can be realized better.
To give you an intuitive understanding, the pros and cons of hardware RAID vs software RAID are summarized in the form below:
Hardware RAID | Software RAID |
Pros: 1. Better performance for more advanced RAID configurations. 2. More RAID configuration options to choose including hybrid configurations that may not be available with some certain OS. 3. Compatible with different OS including Windows and MAC. | Pros: 1. Low cost of entry. 2. Can easily handle RAID 0 and RAID 1 processing. |
Cons: 1. More cost in the initial setup. 2. When using some flash storage arrays, you may encounter inconsistent performance for certain hardware RAID setups. | Cons: 1. It’s often specific to the OS being used. So, it cannot be used for the RAID arrays that are shared between operating systems. 2. The RAID levels that the specific OS can support will be restricted. 3. Not suitable for more complex RAID configuration. |
Software RAID VS Hardware RAID: which is better? Now, I believe that you already have known the answer. No matter you choose software or hardware RAID, you need to manage the RAID drives to get the best performance. How to manage them effectively? Please keep reading the following part.
How to Manage Your RAID Drives Effectively
Although Windows offers a built-in tool (Disk Management) to manage your RAID drives, some features are not available. For example, resizing and extending volume are restricted in some situations. At this time, you need a professional and effective tool to do these works.
Here it’s highly recommended that you choose MiniTool Partition Wizard Server Edition. This powerful software can help you manage RAID partitions ranging from RAID 0 to RAID 6, and other forms like RAID 10 and RAID 50.
Apart from the move/resize feature, this powerful software boasts many other features. It can help you upgrade hard disk, convert MBR to GPT disk, change cluster size without data loss, etc.
If you are limited to resize your volume, you can utilize this program to move or resize the volume easily. Here’s how to do that:
Step 1. Launch this tool to get its main interface, and then select the RAID partition that you want to manage and click on the Move/Resize Volume feature on the left pane.
Step 2. Then you can drag the handle leftward or rightward to resize the volume. If you want to move the volume to the unallocated space, just move the whole handle to change the location. After specifying the volume, click on OK to save the changes.
Step 3. Click on Apply on the upper left corner to execute the operation. After that, you will be asked to restart your computer. You just need to follow the prompt.
What’s Your Opinion
Here comes the end of the post. Today we mainly focus on the software RAID vs hardware RAID. If you have any questions, please send us an e-mail via [email protected]. We also appreciate any ideas left in the comment area.
Hardware VS Software RAID FAQ
Quick Navigation :
RAID Controller
Definition
What is a RAID controller? A RAID controller is a card or chip located between the operating system and a storage drive (usually a hard drive). If you want to get some information about the RAID, you can go to MiniTool’s official website to find it.
What does a RAID controller do? They virtualize drives into different groups with specific data protection and redundancy features. The front-end interface typically communicates with the server through a host-based adapter (HBA). The backend communicates with and manages the underlying storage medium; it is usually ATA, SCSI, SATA, SAS or Fibre Channel.
HighPoint SSD7120 is a bootable Quad M.2 PCIe x16 NVMe SSD RAID card that helps to access your NVMe M.2 drives.
RAID controllers are classified by the multiple characteristics include drive types(such as SATA or SAS), specific RAID levels, and the number of ports and supported drives. The RAID controller is not a storage controller. The storage controller provides the active disk to the system, while the RAID controller acts as a RAM cache and provides RAID functions.
Advantages
Now, let’s see the advantages of the RAID controller card. The hardware-based RAID controller architecture is more expensive than software-based RAID, but it can improve system performance without boot errors. The advantages are as follows:
Cache memory
Removing apps on a mac computer. This tool identifies and removes all junk files related to the app you want to uninstall. In order to remove an app from the Launchpad, you should uninstall it completely from your Mac.We recommend using to safely and correctly remove apps from your Mac.
Controller-based RAID typically provides additional dick cache memory to accelerate RAID operations.
Dedicated processing
The controller-based system independently manages RAID configuration in addition to the operating system. Moreover, the capacity and speed of RAID controllers are superior to software-only RAID since RAID controllers do not require disk processing capabilities.
Lack of boot errors
And, it is affected by boot errors, which can damage the entire array because software-only RAID resides on the operating system. However, RAID controllers will not be affected by boot errors.
Hardware VS Software RAID Controllers
Hardware-Based: RAID Controller
Speed reading software mac deutsch. The dedicated hardware controller has two different architectures: an external RAID Controller Card and an internal RAID-on-chip.
Raid System For Mac
RAID Controller Card: RAID controller card is an expansion card inserted into a PCIe or PCI-X motherboard slot. It has a RAID processor and I/O processor with drive interface.
RAID-on-chip: Cheaper RAID-on-chip is a single motherboard chip with an integrated host interface, HDD I/O interface, RAID processor and memory controller.
Software-Based: Server-Based RAID
Hardware Raid 1
Software RAID provides RAID services from the host. It has two types: software-only RAID and hybrid hardware/software RAID.
Software-only RAID: As a native function on the system, software-only RAID makes the least expensive of the RAID options. The host-based application manages RAID calculations and uses HBA or native I/O interfaces to attach to storage drives.
Hybrid hardware RAID: Hybrid hardware/software RAID delivers RAID BIOS functions from the motherboard or HBA by using a hardware component. Hybrid technology adds another layer and the price of software-only is higher, but it can protect RAID systems from operating system error boot errors.
Different RAID Levels
RAID controllers are specific to RAID levels. The most common levels are RAID 0, 1, 5/6, and 10. The details are as follows:
RAID 0: Striping - RAID 0 is the only RAID level that does not provide redundancy but only improves hard drive performance. RAID 0 divides files and splits data on two or more disks, and treats the divided disks as one partition.
RAID 1: Mirroring – RAID 1 works on two or more desktops to provide data redundancy and failover. It reads and writes the same data to each disk. If the mirrored disk fails, the file will be fully present on a functioning disk.
Raid 5/6: Striping with Parity/Double Parity – RAID 5/6 combines the performance of RAID 0 with the redundancy of RAID 1, but requires about one-third of the available capacity.
RAID 10: Striping and Mirroring - RAID 10 is the most expensive of the RAID levels. It is striped on at least four disks to improve performance and redundant on mirrors. In a four-drive array, the system stripes data to two disks. The remaining two disks mirror the striped disks and each disk stores half of the data.
Also see: Commonly Used Hardware RAID You Should Know
Software Raid Vs Hardware Raid Mac Pro
Final Words
Mac Software Raid Vs Hardware Raid
To sum up, this post mainly introduces some information on the RAID controller include the definition, advantages as well as the different levels. Hence, you will have a comprehensive and deep understanding of the RAID controllers.