Dec 10, 2019 This software has easy to use interface and also contain simple user guide. Just download this amazing bootable USB software now. So these are Best Bootable USB software windows/ Mac 2020 with which you can create bootable USB. Please like, share and comment your views for above listed bootable USB software. Mar 12, 2020 Connect the USB flash drive or other volume that you're using for the bootable installer. Make sure that it has at least 12GB of available storage and is formatted as Mac OS Extended. Open Terminal, which is in the Utilities folder of your Applications folder. Type or paste one of the following commands in Terminal. In this article we'll run through the steps necessary to create a bootable installer of the Mac. On your Mac go to System Preferences Software Update. Drive a name such as 'macOS' or 'USB. 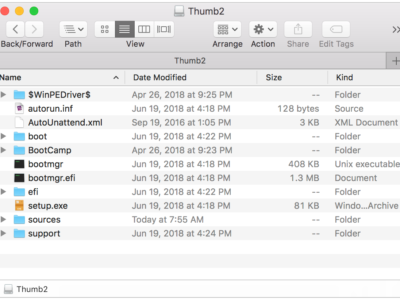 Set it aside, calm down and download a bootable data recovery app using any other computer. Disk Drill is by far the most convenient and up-to-date macOS bootable file rescue solution. It'll make your Mac boot from USB in just a few clicks. Starting with Disk Drill 3, anyone can create a bootable Mac OS X drive in a matter of minutes.
Set it aside, calm down and download a bootable data recovery app using any other computer. Disk Drill is by far the most convenient and up-to-date macOS bootable file rescue solution. It'll make your Mac boot from USB in just a few clicks. Starting with Disk Drill 3, anyone can create a bootable Mac OS X drive in a matter of minutes.
Samsung s5 software free download - Ringtones for Samsung S5, Apple Safari, Lockscreen for S5, and many more programs. GALAXY S5 mini SM-G800H Read first Here you find all the latest Samsung firmwares for the GALAXY S5 mini SM-G800H, if you want to flash your device with the newest Samsung software. Before downloading, make sure your device has the exact model code SM-G800H. Feb 03, 2017 The Samsung Galaxy S5 Mini comes with the latest operating system that is Android v 4.4.3 KitKat. The internal storage or hard drive capacity of galaxy Mini S5 is 16GB. And also it has memory card Slot up to 64 GB for external storage capacity. Galaxy S5 Mini. Samsung Galaxy S5 Software - Free Download Samsung Galaxy S5 - Top 4 Download - Top4Download.com offers free software downloads for Windows, Mac, iOS and Android computers and mobile devices. Visit for free, full and secured software’s. Samsung galaxy s5 mini review.
A site dedicated to learning about microbiology in the laboratory. Remember, there are many ways to make 1/10 and 1/100 dilutions. A 0.1 ml to 0.9 ml dilution is the same as a 1 ml to 9 ml dilution and a 13 ml to 117 ml dilution. EZ-CFU ™ With EZ-CFU ready-to-use reference cultures, Growth Promotion Testing doesn’t have to be a hassle. Delivering 10-100 CFU per 0.1 ml inoculum, following a simple 1:10 dilution step, each microorganism suspension provides up to 90 tests. These handy kits allow for fast, reliable Growth Promotion Testing. Colony forming units (CFU) refer to the number of individual colonies of any microorganism that grows on a plate of media. This number is useful when trying to find how many viable microorganisms are contained within a sample. Plating dilutions of such a sample is a useful method for finding CFU.
How the bacterial growth can be measured?
What are some requirements for microbial growth?
In order to grow successfully, microorganisms must have a supply of water as well as numerous other substances including mineral elements, growth factors, and gas, such as oxygen. Virtually all chemical substances in microorganisms contain carbon in some form, whether they be proteins, fats, carbohydrates, or lipids.Why do you assume that each colony represents a pure culture?
Since all of the cells in a colony derive from a single original cell through repeated binary fission; all of the cells in that colony should be genetically identical. Therefore an ISOLATED colony represents a pure source of an organism from which a pure culture can be started.How the bacterial growth can be measured?
The measurement of an exponential bacterial growth curve in batch culture was traditionally a part of the training of all microbiologists; the basic means requires bacterial enumeration (cell counting) by direct and individual (microscopic, flow cytometry), direct and bulk (biomass), indirect and individual (colony
What is viable count of bacteria?
What is a CFU in microbiology?
In microbiology, a colony-forming unit (CFU, cfu, Cfu) is a unit used to estimate the number of viable bacteria or fungal cells in a sample. Viable is defined as the ability to multiply via binary fission under the controlled conditions.How does a Chemostat work?
A chemostat (from chemical environment is static) is a bioreactor to which fresh medium is continuously added, while culture liquid containing left over nutrients, metabolic end products and microorganisms are continuously removed at the same rate to keep the culture volume constant.What is the CFU ml?
colony-forming unit (CFU or cfu) is a measure of viable bacterial or fungal cells.CFU measures only viable cells. For convenience the results are given as CFU/mL (colony-forming units per milliliter) for liquids, and CFU/g (colony-forming units per gram) for solids.
What is the normal colony count in urine culture?
What antibiotics treat E coli in urine?
Doctors typically treat UTIs with a wide range of different antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin (Cipro) and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim). However, some strains of E. coli, called extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) E. coli, are resistant to most antibiotic treatments.What can be detected in a urine test?
The urinalysis is a set of screening tests that can detect some common diseases. It may be used to screen for and/or help diagnose conditions such as a urinary tract infections, kidney disorders, liver problems, diabetes or other metabolic conditions, to name a few.Do they test for STDS in a urine culture?
Urine Testing for Bacterial STDs. The gold standard for diagnosing bacterial STDs, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, used to be bacterial culture. That involved attempting to grow bacteria out of samples that were taken directly from the cervix or urethra. Even better, they do not require a live bacterial sample.
What is a CFU count?
How many CFU do you need?
What does 1 billion CFU mean?
What is a PFU?
How many cells are in a colony?
 6.
6.How can turbidity be used to count microorganisms?
How does a standard plate count work?
What is a colony of bacteria?
What does CFU stand for what does it mean?
10.Cfu Counting Software
What is the dilution factor?
What is a spread plate?
What is the use of a colony counter?
What is a pure culture in microbiology?
What is the definition of serial dilution?
What is a CFU in education?
What is the abbreviation for CFU?
What is a colony in biology?
What is Colony characteristics?
What is an example of a colony?
What is the size of a bacteria?
Cfu Counting Software For Mac Free
Updated: 4th December 2019